Learning Outcomes in Listing:
i. Describe the process of aerobic respiration including its word and symbol equations.
ii. Understand the stages of aerobic respiration: Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and Electron Transport Chain.
iii. Recognize the role of oxygen and its significance in the production of ATP.
Learning Outcomes Described:
Students will learn about aerobic respiration, a cellular process that uses oxygen to convert the energy stored in glucose into ATP. They will explore each stage of aerobic respiration, including glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain, and will understand how these processes are interlinked to achieve efficient energy conversion.
Summary of Lesson:
Aerobic respiration is a multi-step process that cells use to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into ATP, using oxygen as the final electron acceptor. This lesson will cover the stages of aerobic respiration, detailing how each contributes to the overall production of ATP.
i. Aerobic Respiration Explained:
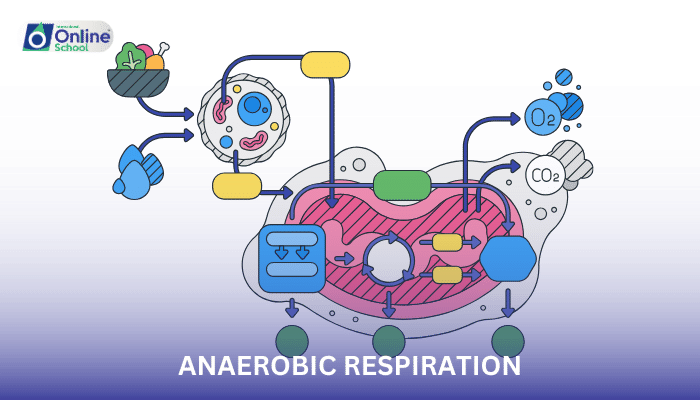
Aerobic respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other molecules in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.
Word and Symbol Equations:
- The word equation for aerobic respiration is:
- Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
- The symbol equation is:
ii. The Mechanism of Respiration:
- Glycolysis: The breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH, occurring in the cytoplasm.
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): A series of reactions that occur in the mitochondrion to produce electron carriers NADH and FADH2 and a small amount of ATP.
- Electron Transport Chain: Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where NADH and FADH2 are oxidized, providing the energy to drive the synthesis of a large amount of ATP.
List of Important Questions for Self-Study:
i. Why is oxygen vital for the process of aerobic respiration?
ii. How do the products of glycolysis enter the Krebs cycle?
iii. What is the significance of the Electron Transport Chain in ATP production?
iv. How is the energy from glucose transferred to ATP during aerobic respiration?
v. What happens to the carbon atoms from glucose by the end of aerobic respiration?
Important Terminologies Used in Lesson:
i. Aerobic Respiration: The process of producing cellular energy involving oxygen.
ii. Glycolysis: The first stage of cellular respiration, where glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvate.
iii. Krebs Cycle: The second stage of aerobic respiration, where pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide.
iv. Electron Transport Chain: The final stage of aerobic respiration, which produces the most ATP.
v. ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): The energy currency of the cell.